Introduction: Why the Form 424B2 Prospectus Deserves Your Attention
If you’ve ever clicked through an SEC filing and felt your eyes glaze over halfway down the page, you’re not alone. Yet hidden inside those dense documents is information that can materially affect investment decisions, capital raises, and regulatory compliance. One such document—the form 424B2 prospectus—is far more important than most people realize.
In real-world finance, this form often shows up at critical moments: a company finalizing a securities offering, an investor evaluating risk before committing capital, or a legal team racing against deadlines to stay compliant. I’ve seen deals delayed, investors confused, and even lawsuits triggered simply because someone misunderstood (or ignored) what was disclosed in a Form 424B2 prospectus.
In this guide, we’re going to slow everything down and make sense of it—plain English, practical examples, and zero legal fog. By the end, you’ll understand what a Form 424B2 prospectus is, why it exists, how to read it confidently, how companies prepare it, and how investors can actually use it to make smarter decisions.
Whether you’re an investor, startup founder, finance student, or compliance professional, this article is designed to feel like advice from someone who’s been in the trenches—not a textbook.
What Is a Form 424B2 Prospectus? A Beginner-Friendly Breakdown
At its core, a form 424B2 prospectus is a detailed disclosure document filed with the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) that provides finalized information about a specific securities offering.
Think of it like this:
If a registration statement is the blueprint for a building, the Form 424B2 prospectus is the final walkthrough before buyers move in.
The Simple Explanation
When a company plans to offer securities (stocks, bonds, notes, or other financial instruments), it first files a broad registration statement—often Form S-3 or Form S-1. That initial filing may leave some details open-ended. Once the company finalizes key terms—pricing, interest rates, maturity dates, underwriting details—it files Form 424B2 to lock those specifics in.
In everyday terms, this form answers questions like:
- Exactly what is being sold?
- At what price?
- Under what risks and conditions?
- How will the proceeds be used?
Why the “B2” Matters
Form 424 has several variations (B1 through B5). The “B2” version is typically used when:
- The offering is made under an existing shelf registration
- The final terms weren’t included in the original prospectus
- The issuer needs to supplement prior disclosures
This makes the Form 424B2 prospectus especially common in large, repeat issuances by public companies and financial institutions.
Why the Form 424B2 Prospectus Matters More Than You Think
It’s easy to assume these filings exist purely to satisfy regulators. In reality, they’re decision-making tools—for both issuers and investors.
For Investors: Your Risk Radar
The Form 424B2 prospectus often contains:
- Updated risk factors
- Final pricing mechanics
- Interest rate structures
- Redemption or call provisions
Missing one clause can mean misunderstanding downside exposure or liquidity constraints. Seasoned investors don’t skim this document—they mine it.
For Companies: Legal and Reputational Protection
From the issuer’s perspective, accuracy here is non-negotiable. Any misleading or incomplete disclosure can trigger:
- SEC enforcement actions
- Investor lawsuits
- Long-term reputational damage
I’ve seen companies spend months repairing trust because of one poorly worded risk disclosure.
For Advisors and Analysts: Due Diligence Gold
Financial analysts, compliance officers, and legal teams rely on the Form 424B2 prospectus to:
- Validate offering structure
- Compare similar issuances
- Ensure alignment with prior filings
In short, this form is where theory meets reality.
Key Components Inside a Form 424B2 Prospectus (And How to Read Them)



4
While formats vary, most Form 424B2 prospectuses include several core sections. Understanding these is half the battle.
Prospectus Summary
This is the executive overview. It outlines:
- The issuer
- The securities offered
- The purpose of the offering
Tip: Read this first, but never stop here. It’s a roadmap—not the destination.
Risk Factors
This section deserves slow, deliberate reading. It explains:
- Market risks
- Issuer-specific risks
- Instrument-specific risks
A red flag isn’t the presence of risks—it’s vague or generic wording that hides real exposure.
Use of Proceeds
Here, the company explains how it plans to use the money raised:
- Debt repayment
- Capital expenditures
- Acquisitions
- General corporate purposes
The more specific this section is, the more confidence it inspires.
Description of Securities
This is where legal precision matters:
- Interest rates or dividends
- Maturity dates
- Conversion features
- Redemption rights
Investors should match this section against their risk tolerance and investment horizon.
Underwriting and Distribution
Details about:
- Underwriters or agents
- Fees and commissions
- Distribution methods
This helps assess incentives and potential conflicts of interest.
Benefits and Real-World Use Cases of the Form 424B2 Prospectus
The value of the Form 424B2 prospectus depends on how you use it. Let’s look at practical scenarios.
Investors Comparing Similar Offerings
Imagine two bonds from similar issuers with nearly identical yields. The Form 424B2 prospectus often reveals subtle differences:
- One allows early redemption
- Another has stricter covenants
- One ties interest to market benchmarks
These nuances can make or break long-term returns.
Startups and Public Companies Raising Capital
For issuers, this form:
- Communicates credibility
- Reduces legal exposure
- Attracts institutional investors
Clear, transparent disclosures can lower perceived risk—and indirectly reduce cost of capital.
Analysts Performing Due Diligence
Equity and debt analysts use Form 424B2 filings to:
- Model cash flows accurately
- Stress-test downside scenarios
- Validate assumptions used in valuations
In professional settings, this form often carries more weight than marketing decks.
How to Prepare and File a Form 424B2 Prospectus: A Step-by-Step Guide


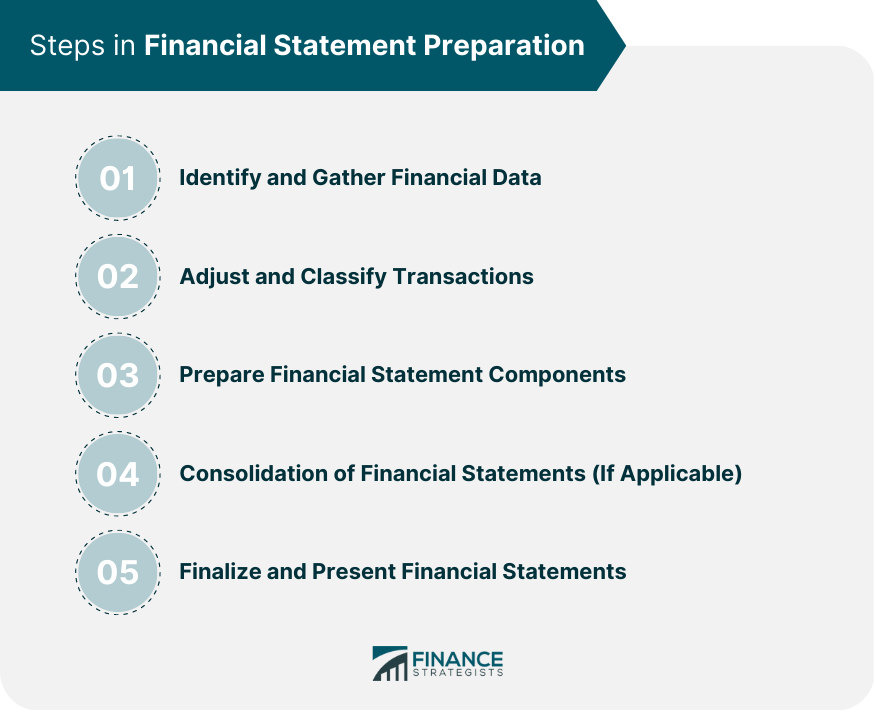
For issuers and advisors, preparing a Form 424B2 prospectus is a structured process.
Step 1: Finalize Offering Terms
Before drafting begins, all material terms must be settled:
- Pricing or interest formulas
- Security structure
- Offering size
Any uncertainty here delays everything downstream.
Step 2: Align With the Base Prospectus
The Form 424B2 supplements an existing registration statement. Consistency is critical:
- Definitions must match
- Risk factors must align
- No contradictions allowed
Step 3: Draft Clear, Accurate Disclosures
This is where legal, finance, and compliance teams collaborate. Best practices include:
- Plain-English explanations
- Explicit risk descriptions
- Conservative assumptions
Step 4: Internal and External Review
Most filings undergo:
- Legal review
- Underwriter review
- Compliance checks
This step often takes longer than expected—plan accordingly.
Step 5: File via EDGAR
Once finalized, the form is filed electronically with the SEC and becomes public record.
Tools, Comparisons, and Expert Recommendations
Professionals rarely handle Form 424B2 prospectuses manually. The right tools matter.
Free Resources
- SEC EDGAR Database
Pros: Official, comprehensive, free
Cons: Not user-friendly for beginners
Paid Platforms
- Financial research terminals
Pros: Searchable, comparative analysis
Cons: Expensive, steep learning curve
My Practical Recommendation
For investors: Start with EDGAR, then layer in summaries from trusted research platforms.
For issuers: Invest in legal and compliance tools—shortcuts here are costly.
Common Mistakes in Form 424B2 Prospectuses (And How to Fix Them)
Even experienced teams make mistakes. Here are the most common ones I’ve seen.
Mistake 1: Treating It as a Formality
Fix: Approach it as an investor-facing document, not a checkbox.
Mistake 2: Overusing Boilerplate Language
Fix: Customize risk factors and disclosures to the specific offering.
Mistake 3: Inconsistent Terminology
Fix: Use a centralized glossary and cross-check definitions.
Mistake 4: Rushing the Filing
Fix: Build in review buffers—errors here are public and permanent.
Conclusion: Mastering the Form 424B2 Prospectus Is a Competitive Advantage
The form 424B2 prospectus isn’t just another SEC filing—it’s a bridge between regulatory compliance and informed decision-making. Investors who read it carefully gain clarity others miss. Companies that prepare it thoughtfully earn credibility and trust.
If there’s one takeaway from this guide, it’s this: slow down, read deeply, and respect the details. In finance, the fine print isn’t where problems hide—it’s where the truth lives.
If you’ve found this guide useful, consider bookmarking it, sharing it with a colleague, or diving into a real Form 424B2 filing and practicing what you’ve learned.
FAQs
What is the purpose of a Form 424B2 prospectus?
It provides finalized details of a securities offering that weren’t included in the original registration statement.
Who is required to file Form 424B2?
Public companies and issuers offering securities under certain SEC registration frameworks.
Is Form 424B2 mandatory for all offerings?
No, only for offerings that meet specific criteria under SEC rules.
How does Form 424B2 differ from Form 424B1?
Form 424B2 typically supplements shelf registrations, while B1 has different timing and disclosure rules.
Where can I find a Form 424B2 prospectus?
On the SEC’s EDGAR database under the issuer’s filings.
Michael Grant is a business writer with professional experience in small-business consulting and online entrepreneurship. Over the past decade, he has helped brands improve their digital strategy, customer engagement, and revenue planning. Michael simplifies business concepts and gives readers practical insights they can use immediately.






