If you’ve ever tried to build an app, launch a website, or even explore careers in tech, chances are you’ve heard the term “tech stack.” And if your first thought was “Okay, but what does that actually mean?”—you’re not alone.
Not long ago, a freelance client asked me to help evaluate the “tech stack” behind their online store. They spoke about it the way a car enthusiast talks about engine parts, while I sat there thinking: I know this matters… but why?
That moment pushed me to dig deep into what tech stacks are, how they work, and why they’re one of the most foundational concepts in modern technology. Whether you’re a business owner, aspiring developer, product manager, or curious learner, understanding What Is a Tech Stack is can save you money, improve performance, speed up development, and help you make better long-term decisions.
In this guide, we’ll break it all down in the simplest, most human way possible—no jargon, no overcomplication—just clear, practical knowledge you can actually use.
What Is a Tech Stack? (Beginner-Friendly Explanation)

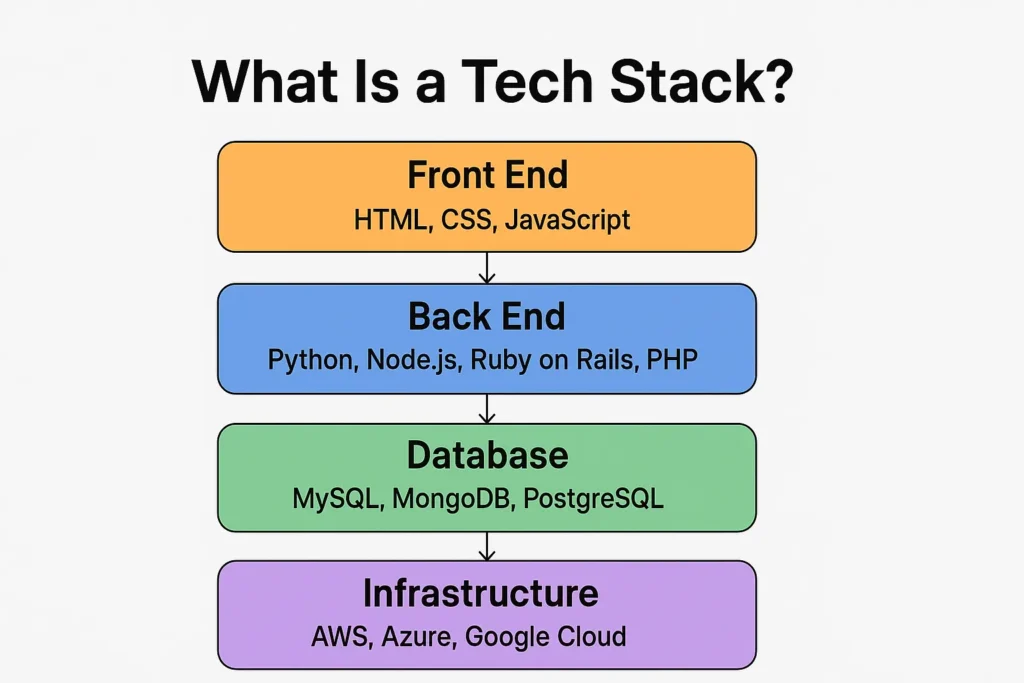
A tech stack—short for technology stack—is the combination of tools, programming languages, frameworks, and software used to build and run a digital product.
Think of it as the recipe behind a website or app.
Just like a chef chooses ingredients (flour, eggs, spices) and tools (oven, mixer, pan) to make a dish, developers choose a collection of technologies to create a digital experience.
A tech stack typically includes:
- Front-end technologies — what users see and interact with
- Back-end technologies — what works behind the scenes
- Databases — where data is stored
- Infrastructure & DevOps tools — how the system runs, scales, and stays secure
A simple way to visualize it:
Front End = the storefront of a shop
Back End = the storeroom, staff, and systems you don’t see
Database = the inventory
Infrastructure = the building, electricity, and security
Together, these components make up the stack—layer upon layer of technology working together to power your product.
Why Tech Stacks Matter (Even If You’re Not a Developer)
You might think tech stacks are “developer stuff,” but they affect nearly every part of your digital business or career.
Here’s why understanding them matters:
1. They determine performance
A slow tech stack = a slow website or app.
A fast, modern tech stack = smoother user experience and better conversions.
2. They impact development cost
Some stacks require highly specialized developers (expensive).
Others rely on widely available skills (cost-effective).
3. They influence scalability
If you plan to grow, your tech must grow with you.
Some stacks scale beautifully. Others crack under pressure.
4. They affect maintainability
Old or poorly chosen technologies can create “technical debt”—the digital version of a messy garage nobody wants to clean.
5. They shape hiring decisions
If your stack uses rare technologies, finding talent becomes harder.
6. They directly impact business ROI
The right stack saves money, improves reliability, and shortens development time.
In short:
Tech stacks are the foundation of every digital product. Get the foundation wrong, and everything above it feels shaky.
Breaking Down a Tech Stack: Front End vs. Back End
Let’s walk through the two main sides of a tech stack.
Front-End (Client-Side) Tech Stack: What Users See
This is everything that appears in the browser or app screen.
Common front-end technologies include:
- HTML — the structure
- CSS — the design/style
- JavaScript — the interactivity
Developers often enhance JavaScript with frameworks like:
- React
- Vue.js
- Angular
- Svelte
Analogy:
If your app were a restaurant, the front end is the dining area—decor, music, lighting, menu, and everything customers see.
Back-End (Server-Side) Tech Stack: What Users Don’t See
This is the engine powering your product—processing logic, storing data, handling logins, and more.
Common back-end technologies include:
- Node.js
- Python (Django, Flask, FastAPI)
- Ruby on Rails
- PHP (Laravel)
- Java
- C# / .NET
Back-end development also includes databases such as:
- MySQL
- PostgreSQL
- MongoDB
- Redis
Analogy:
The back end is your restaurant’s kitchen—busy, messy, stressful, but absolutely essential for making the whole thing work.
Infrastructure Tools: Hosting, Deployment & Scaling
Even the best code needs a place to live. That’s where infrastructure comes in:
- AWS, Google Cloud, Azure — cloud giants
- Docker — packaging apps
- Kubernetes — managing containers
- Vercel, Netlify — modern hosting for front-end apps
- Cloudflare — security, performance, CDNs
Analogy:
Infrastructure is the physical building, electricity, plumbing, and security systems. Without them, even the best restaurant can’t operate.
Real-World Tech Stack Examples
Let’s look at real-world examples to make this concrete.
Example 1: A Simple Business Website
- Front end: HTML, CSS, vanilla JavaScript
- CMS: WordPress
- Hosting: Bluehost or SiteGround
- Database: MySQL
Perfect for: small businesses, blogs, portfolios.
Example 2: A Modern SaaS Product
- Front end: React + TypeScript
- Back end: Node.js or Python
- Database: PostgreSQL
- Infrastructure: AWS + Docker
- Auth: Auth0
- Payments: Stripe
Perfect for: SaaS startups, scalable apps.
Example 3: An E-commerce Platform
Option A: Shopify (all-in-one)
Option B: Custom stack:
- Front end: Next.js
- Back end: Node.js or Laravel
- Database: MySQL or MongoDB
- Platform: Vercel + AWS
- Tools: Stripe, Klaviyo, Shippo
Perfect for: growing brands needing flexibility.
Benefits of Choosing the Right Tech Stack
Choosing the right tech stack is like choosing the right foundation for a house. Do it right, and everything becomes easier.
1. Faster development
Modern stacks come with pre-built components and strong documentation.
2. Better performance
A good stack improves site speed, uptime, and responsiveness.
3. Improved security
Some technologies have built-in security features or mature communities providing updates.
4. Scalability
When your user base grows, your stack should handle the load effortlessly.
5. Easier hiring and collaboration
Popular stacks attract more talent, reducing cost and complexity.
6. Lower long-term costs
Good architecture reduces bugs and maintenance overhead.
Who Should Care About Tech Stacks?
You might be surprised: it’s not just developers.
Entrepreneurs & business owners
Helps you make smarter decisions when hiring agencies or developers.
Project & product managers
Allows you to better plan timelines, resources, and budgets.
Developers & technical students
Expands your career options and deepens your understanding of system architecture.
Investors
A weak tech stack can be a red flag for scalability.
Marketers & SEO specialists
Tech choices impact page speed, SEO score, and tracking tools.
In short:
If you work anywhere near digital products, understanding tech stacks gives you an edge.
How to Choose the Right Tech Stack (Step-by-Step Guide)
Choosing a tech stack doesn’t have to feel overwhelming. Use this practical framework.
Step 1: Define the goal of your product
Ask:
- Is this a small website or a large-scale application?
- Do you need speed, security, or complex functionality?
- Are you building an MVP or a long-term platform?
Your goals shape your stack.
Step 2: Evaluate your team’s skills
The best stack is often the one your team already knows well.
If your developers are experts in Python, forcing them to build in Java makes little sense.
Step 3: Consider time-to-market
If speed matters:
- Use frameworks with lots of reusable components
- Choose hosted platforms like Firebase, Vercel, or Shopify
Step 4: Assess scalability needs
If you plan to grow fast:
- Choose cloud-native solutions
- Use languages/frameworks known for performance
Step 5: Consider community support & documentation
You want technologies that:
- Have active communities
- Receive regular updates
- Offer strong troubleshooting resources
This reduces friction and accelerates development.
Step 6: Evaluate long-term costs
Think beyond development:
- maintenance
- hosting fees
- developer salaries
- security
- updates
A cheap stack today can become expensive tomorrow.
Step 7: Test before committing
Build a small prototype or MVP.
Validate performance, speed, and team fit before diving in fully.
Common Tech Stack Tools & Recommendations
Here’s a human, honest breakdown of common choices.
Best Front-End Tools
- React: Most popular, flexible, tons of libraries
- Vue: Easy for beginners
- Next.js: Excellent for SEO and server-side rendering
- Svelte: Lightweight and blazing fast
Best Back-End Tools
- Node.js: Great for full-stack JavaScript
- Python (Django/FastAPI): Fast development, beginner-friendly
- Ruby on Rails: Rapid prototyping
- Laravel: Great for PHP developers
Best Databases
- PostgreSQL: Most reliable all-rounder
- MySQL: Classic, widely supported
- MongoDB: Flexible, great for unstructured data
Best Cloud Platforms
- AWS: Most powerful
- Google Cloud: Great for AI & data
- Azure: Best for enterprise/MS ecosystems
- Vercel & Netlify: Perfect for front-end hosting
Free vs. Paid Options
| Need | Free Tools | Paid Tools |
|---|---|---|
| Hosting | Vercel (free tier), Netlify | AWS, DigitalOcean |
| Databases | PostgreSQL, MySQL | Managed DBs like AWS RDS |
| Authentication | Firebase Auth | Auth0 |
| E-commerce | WooCommerce | Shopify |
| Analytics | Plausible (cheap), GA4 | Mixpanel, Amplitude |
Free tools are great for MVPs.
Paid tools are great for scale, reliability, and support.
Common Mistakes People Make With Tech Stacks (and How to Fix Them)
Mistake 1: Choosing a stack because it’s trendy
Framework FOMO is real. But trends don’t equal good decisions.
Fix: Choose based on your goals, not hype.
Mistake 2: Mixing too many tools
More tools = more complexity, bugs, and maintenance.
Fix: Keep it lean. Start simple, scale later.
Mistake 3: Using outdated technologies
Legacy systems = slow performance + security issues.
Fix: Choose tools with active communities and updates.
Mistake 4: Not planning for scalability
A stack that works for 100 users may not work for 100,000.
Fix: If growth is expected, choose scalable infrastructure early.
Mistake 5: Ignoring documentation & community
Tools without support become bottlenecks.
Fix: Always check documentation quality before committing.
Mistake 6: Over-engineering the MVP
Many founders build enterprise-level stacks for tiny prototypes.
Fix: Build lean MVPs. Upgrade when traction hits.
Conclusion: Why Understanding Tech Stacks Gives You an Advantage
A tech stack isn’t just a list of tools—it’s the backbone of your digital product.
When you understand what a tech stack is and how it works, you make smarter decisions, communicate more clearly with developers, and build digital experiences that grow with your business.
Whether you’re launching a startup, managing a website, or exploring a tech career, knowledge of tech stacks is a true superpower—one that pays off in speed, performance, cost savings, and long-term success.
If you have questions or want help choosing the right stack for your project, feel free to comment or reach out. I’m always happy to guide you.
FAQs
What is a tech stack in simple terms?
A tech stack is the combination of technologies—front end, back end, database, and infrastructure—used to build a digital product.
Why is choosing the right tech stack important?
It affects performance, cost, development speed, scalability, and maintenance.
What are the most common tech stacks?
MERN (MongoDB, Express, React, Node) and LAMP (Linux, Apache, MySQL, PHP) are classic examples.
What is the best tech stack for beginners?
HTML, CSS, JavaScript, and a Python or Node.js back-end framework.
Can a tech stack be changed later?
Yes, but it can be expensive or complex. Choosing well early saves time and money.
Adrian Cole is a technology researcher and AI content specialist with more than seven years of experience studying automation, machine learning models, and digital innovation. He has worked with multiple tech startups as a consultant, helping them adopt smarter tools and build data-driven systems. Adrian writes simple, clear, and practical explanations of complex tech topics so readers can easily understand the future of AI.